A disposable nasopharyngeal airway (NPA) is a medical device designed to maintain or open a patient’s airway by providing a clear passage from the nostril to the nasopharynx. It is commonly used in emergency and pre-hospital settings, as well as in anesthesia and critical care, to ensure that the sterile airway remains unobstructed, especially in patients who are semi-conscious or unconscious and at risk of airway obstruction.


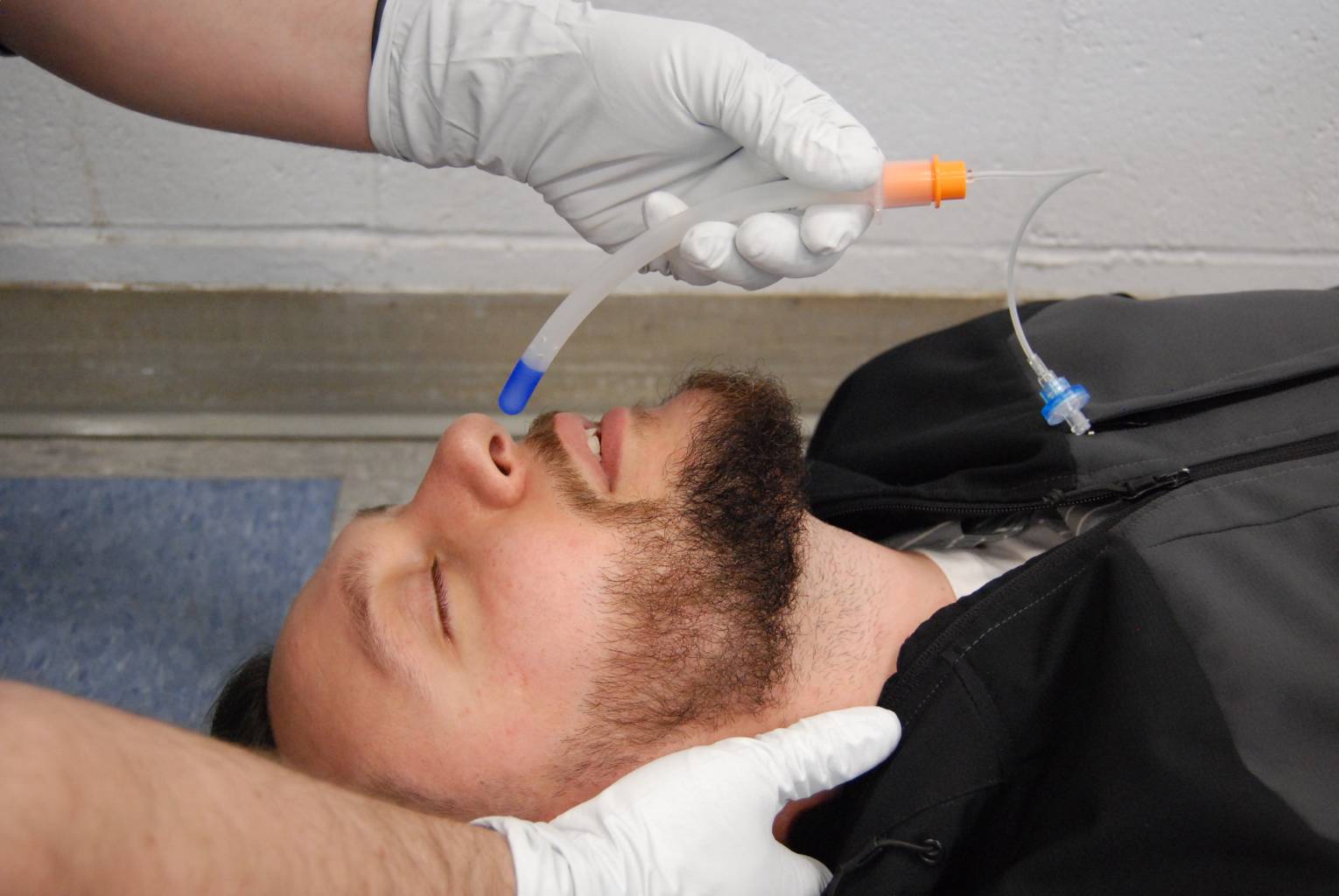
Quick Insertion: Disposable sterile nasopharyngeal airways can be rapidly inserted by trained personnel, making them ideal for emergency situations where time is critical.
Tolerability: Disposable nasopharyngeal airways are generally better tolerated by semi-conscious or unconscious patients compared to oropharyngeal airways, which can trigger a gag reflex.
Various Sizes: Available in various sizes to fit different patient anatomies, from pediatric to adult, ensuring that an appropriate size can be selected for each patient.
Multiple Applications: Useful in a variety of settings, including pre-hospital care, emergency rooms, anesthesia, and critical care units.
Disposable: Disposable sterile nasopharyngeal airways are designed for single-use, which significantly reduces the risk of cross-contamination and infection compared to reusable devices.
Less Invasive: Compared to endotracheal intubation, disposable nasopharyngeal airways are less invasive and can be inserted without the need for advanced airway management skills or equipment.
Three-way connector: In addition to connecting it to the carbon dioxide collection tube, the closed cover can also be opened for suctioning sputum, fiberoptic bronchoscope insertion and other operations, so that the nasopharyngeal tube has a better guiding role when inserted through the nose, with less trauma
Bilateral opening: Reduces the chance of the outlet end being compressed and blocked, ensuring air flow
Conical spherical tip: So that the nasopharyngeal tube has a better guiding role when inserted through the nose, with less trauma, and the tip has a supporting and protective effect on the outlet end
Product Name | Disposable sterile nasopharyngeal airway, Pre-Lubricated Nasal Airway, Nasopharyngeal Airway Kits |
Size | 4.0mm, 5.0mm, 5.5mm, 6mm, 6.5mm, 7.0mm |
Color | Clear |
Material | Medical Grade PVC |
Grade | Class II |
Sterilization | EO sterilized |
Type | General type, monitoring type |
Connector type | Straight connector, a three-way connector |
Suitable for | Adults, Children |
Composition | General type: ① Vent tube ② Straight connector ③ three-way connector ④ Sealable cap ⑤ Luer plug Monitoring type: ① Vent tube ② Monitoring catheter③ Straight connector |
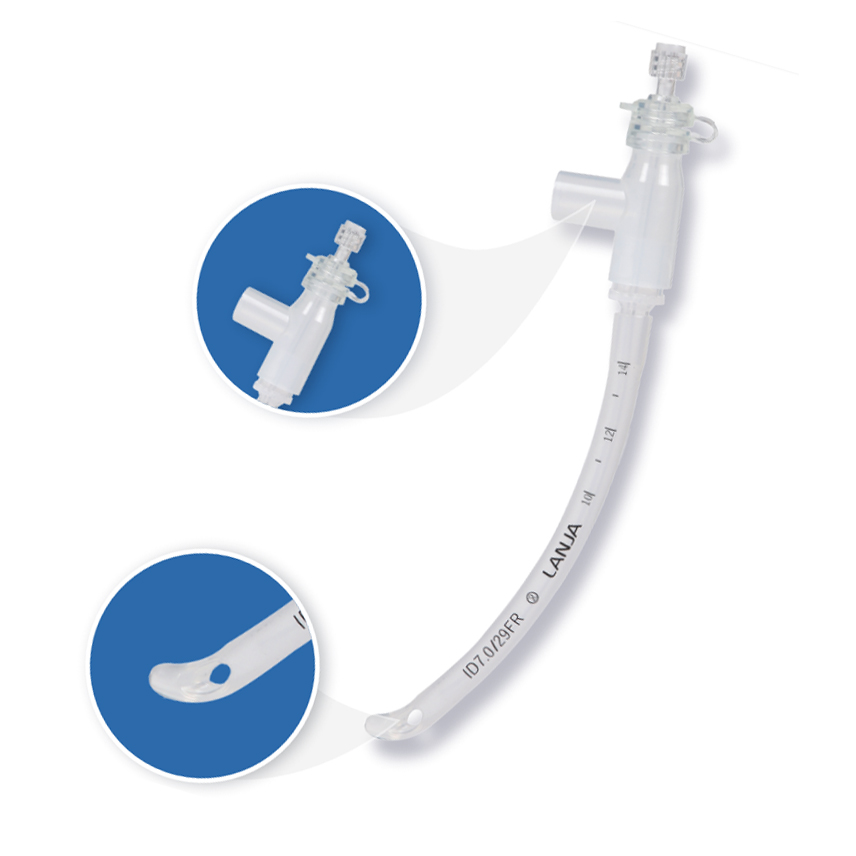

Disposable Nasopharyngeal Airway Made from soft, flexible medical-grade PVC material, the NPA is designed to minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of injury to your nasal passages.
PVC is a flexible, durable and affordable material. It is widely used in medical devices due to its versatility and ease of manufacture. It is easy to insert, which reduces the risk of injury to the nasal mucosa. It resists tearing and deformation, ensuring that the airway remains open.
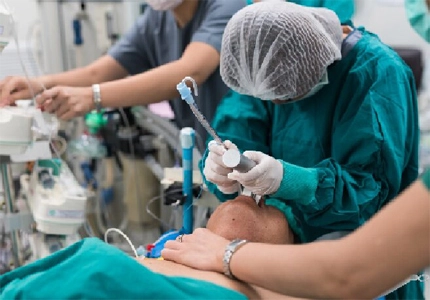
Suitable for patients who are at risk of airway obstruction, establishing an oropharyngeal airway for patients with airway obstruction
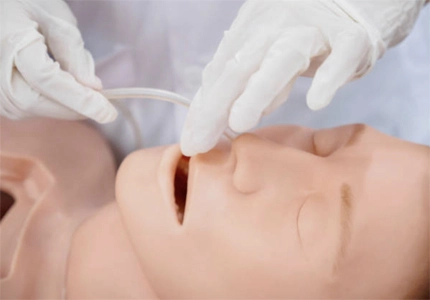
Used in medical education and simulation training to teach airway management techniques to healthcare providers.

NPAs are often used by paramedics and emergency medical technicians (EMTs) to secure the airway of patients in pre-hospital settings, especially when the patient is semi-conscious or unconscious.
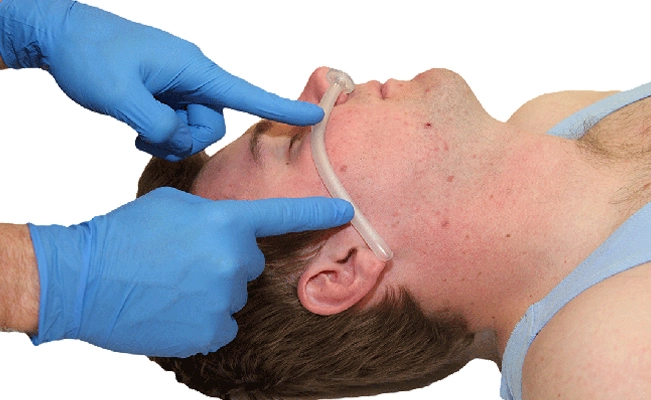
Measure from the tip of the patient’ s nose to the earlobe or the angle of the jaw. This helps ensure the nasopharyngeal airway is the correct length. Choose the size that best fits the patient.
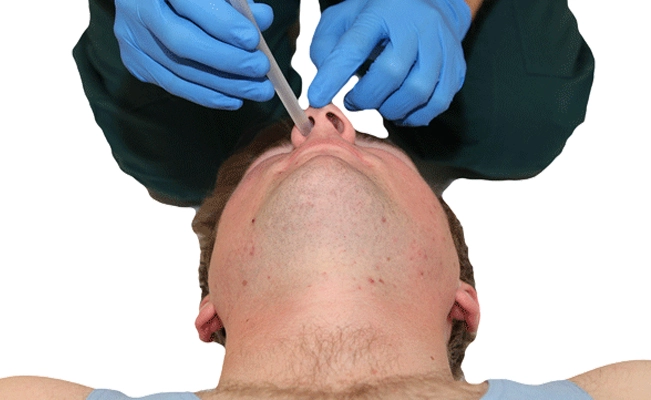
Hold the NPA with the beveled tip pointing towards the septum (the center of the nose).Gently insert the NPA into the nostril. Advance the NPA until the flange rests against the nostril.
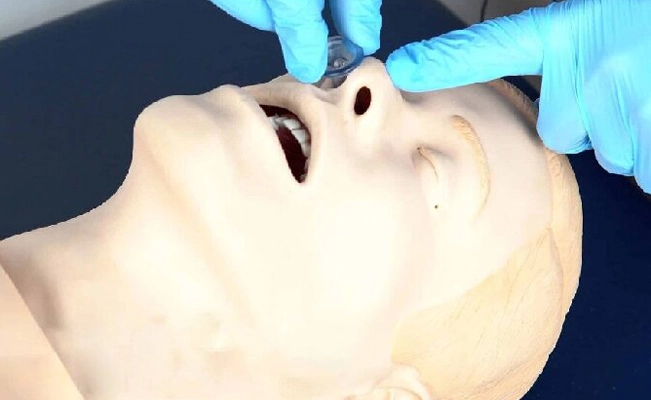
Observe the patient’ s chest for rise and fall, indicating effective ventilation. Listen for breath sounds to ensure air is passing through the NPA.Monitor the patient for any signs of distress or discomfort.