A hospital bed is a specialized piece of furniture designed for patients in medical facilities. It typically consists of a sturdy metal frame with adjustable features to provide comfort and support for patients during their stay.
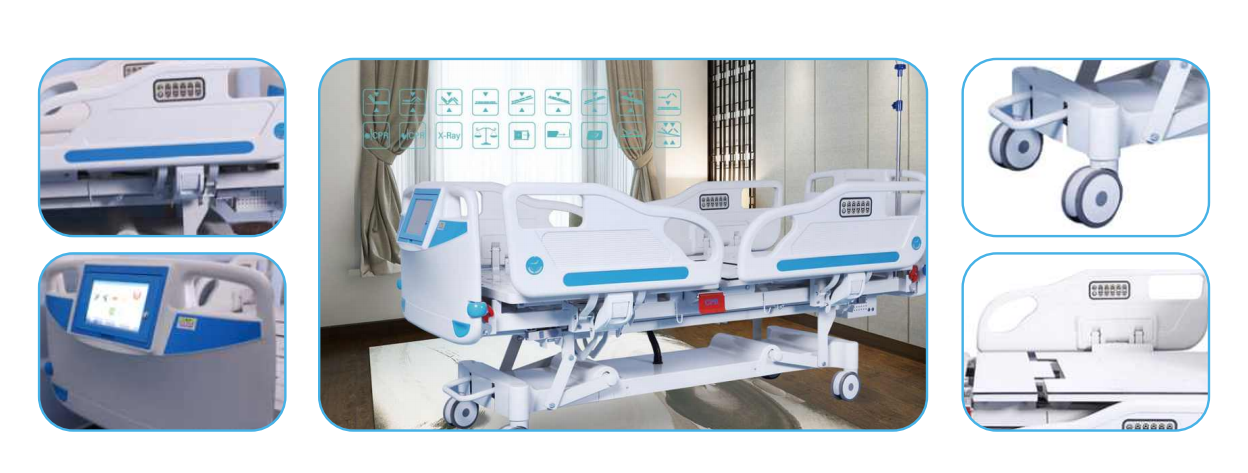



Adjustable height: Hospital beds can be raised or lowered to accommodate the height requirements of patients and healthcare providers. This feature allows for easier patient transfers and accessibility.
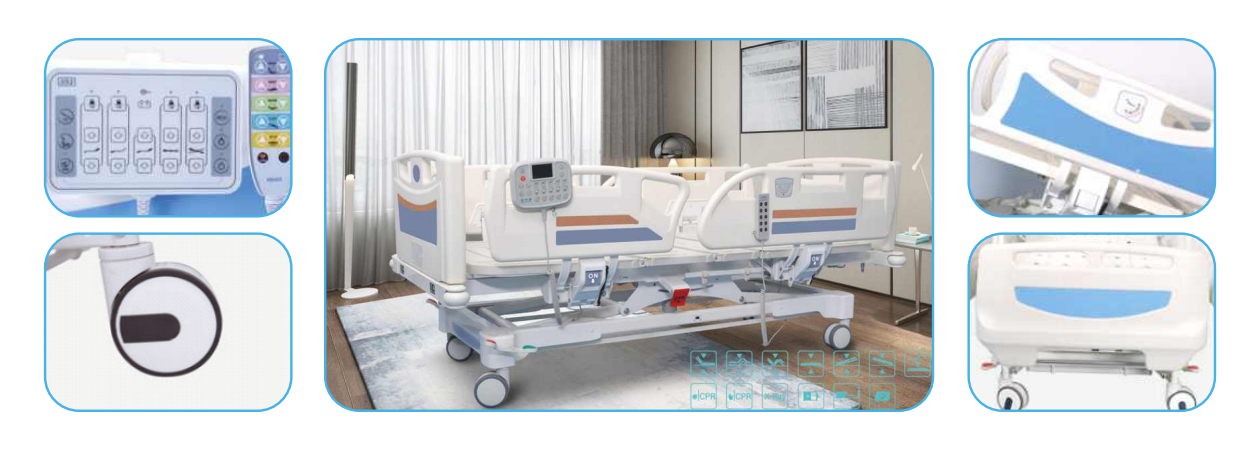
Head and foot adjustments: Hospital beds often have mechanisms that allow the head and foot sections to be raised or lowered independently. This feature enables patients to find a comfortable position for activities like eating, reading, or watching TV.
Side rails: Many hospital beds come with side rails that can be raised or lowered to provide safety and prevent patients from falling out of bed. These rails can be easily adjusted and locked into position.
Trendelenburg and reverse Trendelenburg positions: Some hospital beds have the ability to tilt the entire bed frame to create a Trendelenburg position (head down, feet up) or a reverse Trendelenburg position (head up, feet down). These positions are often used for specific medical procedures or to improve patient comfort.
Wheels and brakes: Hospital beds are equipped with wheels that allow for easy mobility within the facility. The wheels can be locked in place with brakes to ensure stability and prevent unintended movement.
Weight capacity: Hospital beds are designed to support different weight capacities, ranging from standard to bariatric options. This feature ensures that the bed can safely accommodate patients of various sizes.
Mattress options: Hospital beds typically come with a specialized mattress designed for medical use. These mattresses are often made of foam or pressure-relieving materials to prevent bedsores and provide comfort for patients.
Remote control: Some hospital beds come with a remote control that allows patients or caregivers to adjust the bed’s height, head, and foot positions without manually operating the bed.
Accessories: Hospital beds may have additional accessories like overbed tables, IV poles, or patient lift systems that can be attached to the bed frame for convenience and enhanced patient care.
These features may vary depending on the specific model and brand of the hospital bed.



.png)
Hospital beds are typically made of sturdy and durable materials to ensure stability, strength, and ease of cleaning. The main materials used in the construction of hospital beds include:
Metal: Hospital bed frames are commonly made of metal, such as steel or aluminum. These metals provide strength and durability to support the weight of patients and withstand heavy use in medical settings.
Plastic: Certain parts of hospital beds, such as the side rails or control panels, may be made of high-quality plastic. Plastic is lightweight, easy to clean, and resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for these components.
Fabric: The mattress and upholstery of hospital beds are often made of fabric materials that are designed to be comfortable, breathable, and easy to clean. These fabrics are typically treated to be stain-resistant and antimicrobial to maintain a hygienic environment.
Foam: Hospital bed mattresses are often made of foam materials that provide support and pressure relief for patients. These foams are designed to distribute weight evenly and prevent the development of bedsores.
Rubber: Some hospital beds may have rubberized components, such as grips or bumpers, to provide added safety and protection against accidental bumps or falls.

Patient care: Hospital beds are primarily used for providing comfortable and safe resting and sleeping surfaces for patients in hospitals, clinics, and other medical facilities. They are designed to support patients who may have limited mobility, are recovering from surgery or illness, or require ongoing medical monitoring and treatment.
Medical procedures: Hospital beds are often used during medical procedures that require patients to be in a specific position or require easy access to the patient’s body. The adjustable features of hospital beds, such as the ability to raise or lower the head or foot sections, make it easier for healthcare providers to perform procedures or examinations.

Rehabilitation: Hospital beds are commonly used in rehabilitation settings to assist patients in their recovery process. These beds can be adjusted to different positions to facilitate exercises, transfers, and therapy sessions.
Palliative care: Hospital beds play a crucial role in providing comfort and support for patients receiving palliative or end-of-life care. The adjustable features allow caregivers to position patients in a way that minimizes pain and discomfort.

Long-term care: Hospital beds are often used in long-term care facilities, nursing homes, and assisted living centers to provide a comfortable and safe sleeping surface for residents who may have chronic illnesses or mobility issues.
Home healthcare: Hospital beds can also be used in home healthcare settings, allowing patients to receive medical care and support in the comfort of their own homes. These beds can be beneficial for individuals with chronic conditions or those recovering from surgery or illness.
Overall, hospital beds are versatile and essential equipment in healthcare settings, providing comfort, safety, and support for patients during their medical treatment, recovery, and long-term care.
Adjusting the height: To adjust the height of the bed, locate the height adjustment mechanism, which is usually located on the bed frame or control panel. Use the appropriate controls or levers to raise or lower the bed to the desired height. Ensure that the bed is at a comfortable and safe level for the patient and caregivers.
Adjusting the head and foot sections: Most hospital beds have mechanisms to adjust the head and foot sections independently. Locate the controls or levers for these adjustments, usually found on the bed frame or control panel. Use these controls to raise or lower the head and foot sections to the desired position for patient comfort or medical procedures.
Using side rails: If the bed is equipped with side rails, ensure they are properly raised and locked into position to prevent the patient from falling out of bed. To raise or lower the side rails, locate the release mechanism and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper operation.
Locking the wheels: If the bed has wheels, ensure that they are locked in place to prevent unintended movement. Engage the wheel locks by pressing down on the brake pedals or levers located near the wheels. Verify that the bed is stable and secure before leaving the patient unattended.

Adjusting the height: To adjust the height of the bed, locate the height adjustment mechanism, which is usually located on the bed frame or control panel. Use the appropriate controls or levers to raise or lower the bed to the desired height. Ensure that the bed is at a comfortable and safe level for the patient and caregivers.
Adjusting the head and foot sections: Most hospital beds have mechanisms to adjust the head and foot sections independently. Locate the controls or levers for these adjustments, usually found on the bed frame or control panel. Use these controls to raise or lower the head and foot sections to the desired position for patient comfort or medical procedures.
Using side rails: If the bed is equipped with side rails, ensure they are properly raised and locked into position to prevent the patient from falling out of bed. To raise or lower the side rails, locate the release mechanism and follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper operation.
Locking the wheels: If the bed has wheels, ensure that they are locked in place to prevent unintended movement. Engage the wheel locks by pressing down on the brake pedals or levers located near the wheels. Verify that the bed is stable and secure before leaving the patient unattended.