An oxygen flowmeter is a medical device used to measure and regulate the flow rate of oxygen being delivered to a patient. It is an essential component in various healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, and home care environments, where precise oxygen delivery is crucial for patient care.
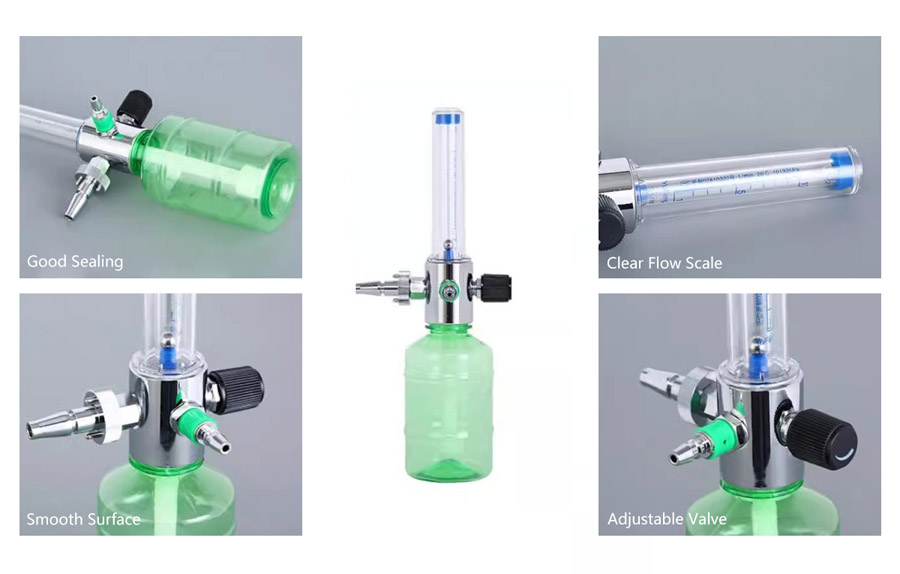



Precise Flow Control
Oxygen flowmeters provide accurate readings of oxygen flow rates, ensuring that patients receive the exact amount of oxygen prescribed by healthcare providers.
Improved Safety
Oxygen flowmeters are designed with safety features to handle high-purity oxygen, reducing the risk of combustion or contamination.
Enhanced Efficiency
By providing accurate flow measurements, oxygen flowmeters help optimize oxygen usage, reducing waste and improving process efficiency.
Compatibility with Various Systems
Oxygen flowmeters can be integrated with different oxygen delivery systems, such as nasal cannulas, masks, ventilators, and industrial pipelines.
Ease of Use:
Simple and intuitive controls make it easy for healthcare providers and caregivers to operate the flowmeter.
Improved Patient Comfort:
Optional humidifier bottles can be attached to some flowmeters to add moisture to the oxygen, preventing dryness and irritation in the patient’s airways.
Product Name | Oxygen Flowmeter / Medical Air Flow Meter |
Material | Brass |
Sensor | Plug-in |
Gas Type | Medical Air |
Output Pressure | 0.2~0.3MPa |
Flow Range | 1~10L/min, 0~15L/min, 0~25L/min, 0~60L/min |
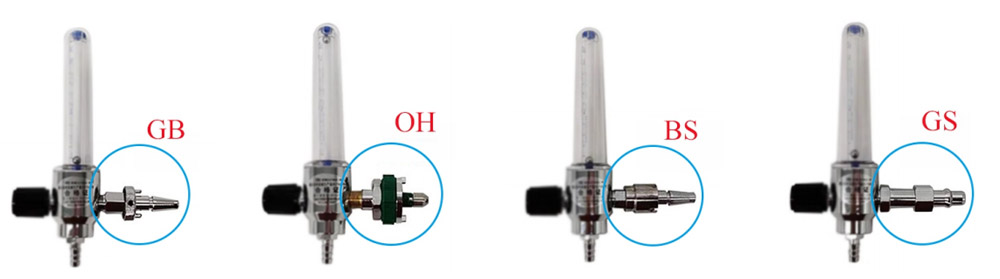
Adaptor | Optional (GB, OH, BS, DIN etc.) |

Flow Tube:
Glass: Often used for its clarity and resistance to scratching. Glass flow tubes provide excellent visibility for reading the flow rate.
Polycarbonate or Acrylic: These durable plastics are also used for flow tubes due to their impact resistance and clarity. They are lighter and less prone to breakage compared to glass.
Flow Indicator (Ball or Bobbin):
Stainless Steel: Commonly used for its durability, corrosion resistance, and weight, which ensures accurate flow rate readings.
Plastic (e.g., Nylon or Teflon): Lightweight and resistant to wear and tear, these materials are also used for the floating ball or bobbin.
Flow Control Knob/Valve:
Brass: Often used for its strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Brass valves provide precise control over the flow rate.
Stainless Steel: Used for its corrosion resistance and durability, especially in high-quality flowmeters.
Plastic: Some flowmeters use high-strength plastics for the control knob to reduce weight and cost.
Body and Housing:
Aluminum: Lightweight and durable, aluminum is commonly used for the main body of the flowmeter.
Brass: Provides excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, making it suitable for the body and internal components.
Plastic (e.g., Polycarbonate or ABS): Used in some models for the outer housing to reduce weight and cost while maintaining durability.
Inlet and Outlet Ports:
Brass: Commonly used for its durability and ability to form tight, leak-proof connections.
Stainless Steel: Used for its strength and corrosion resistance, especially in high-quality or specialized flowmeters.
Seals and O-Rings:
Silicone: Used for its flexibility, durability, and resistance to temperature extremes.
Neoprene or Nitrile Rubber: Commonly used for their resistance to oils and gases, ensuring a tight seal.
Humidifier Bottle (Optional):
Polycarbonate or Polypropylene: These plastics are used for their durability, impact resistance, and ability to withstand the humidification process.
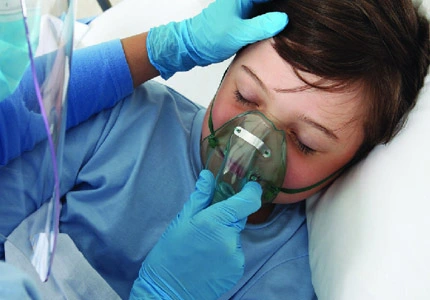
Oxygen flow meters are essential for oxygen therapy for patients with respiratory conditions. The flow meter ensures that the patient is receiving the correct amount of oxygen prescribed by the healthcare provider.
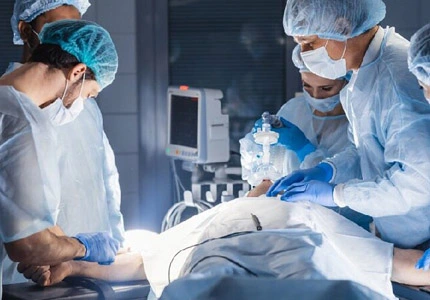
In surgical settings, oxygen flowmeters are used as part of anesthesia machines to deliver a precise mixture of oxygen and anesthetic gases to patients undergoing surgery.
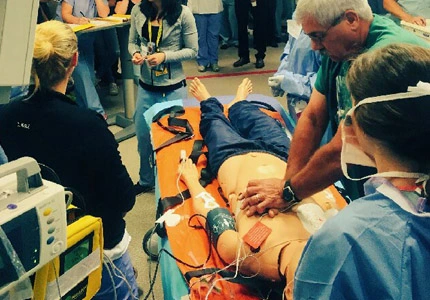
In emergency situations, such as trauma, cardiac arrest, or acute respiratory distress, oxygen flowmeters are used to provide immediate oxygen support to stabilize the patient’s condition.
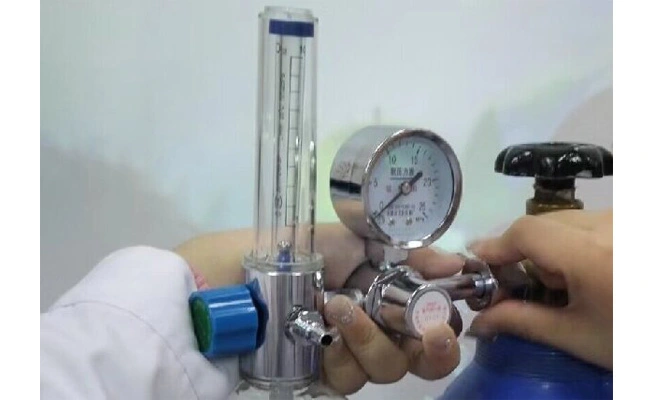

Tighten the oxygen inlet screw to the oxygen cylinder and open the oxygen cylinder valve
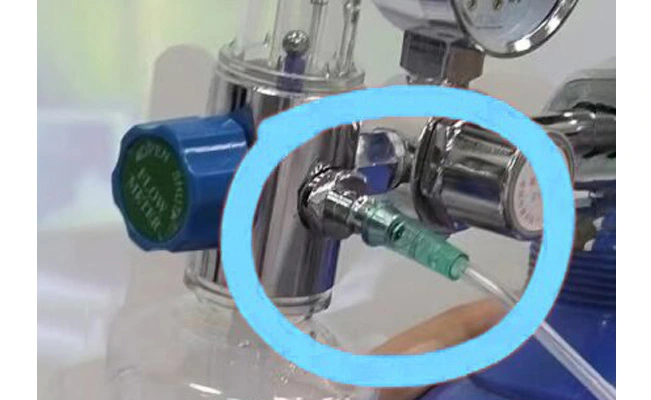
Insert the oxygen tube into the oxygen outlet and connect it tightly
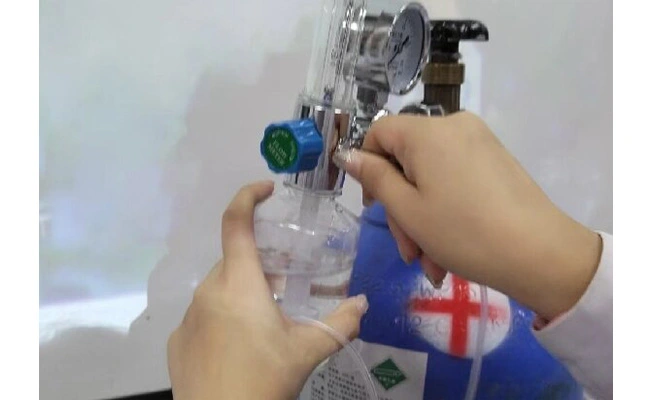

Screw down humidifier, add pure water until between upper and lower water line, then screw the humidifier with the cap of the humidifier tightly
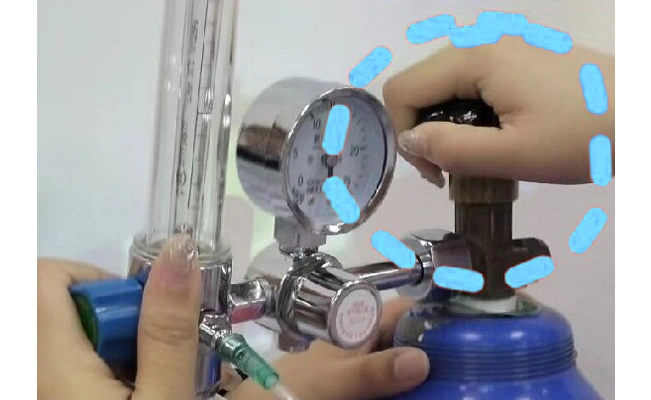

Adjust the flow regulator to the required flow and inhale oxygen through the oxygen tube
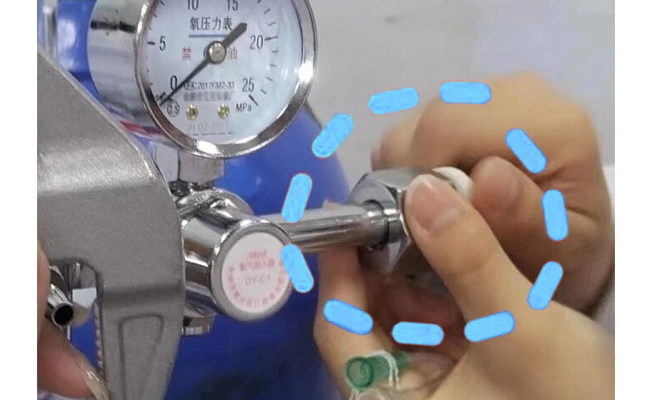

After stopping oxygen inhalation, close the oxygen cylinder valve and close the flow regulator when the pressure gauge pointer points to "0"